Step 1: Create Bootable USB Drive
- Start PowerISO (v6.5 or newer version, download here).
- Insert the USB drive you intend to boot from.
- Choose the menu "Tools > Create Bootable USB Drive". The "Create Bootable USB Drive" dialog will popup. If you are using Windows Vista or above operating system, you need confirm the UAC dialog to continue.
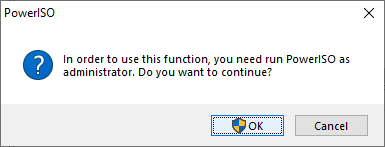
- In "Create Bootable USB Drive" dialog, click "..." button to open the iso file of Windows operating system.
- Select the correct USB drive from the "Destination USB Drive" list if multiple USB drives are connected to the computer.
- Choose the proper writing method. "USB-HDD" is recommended.
- Click "Start" button to start creating bootable USB drive.
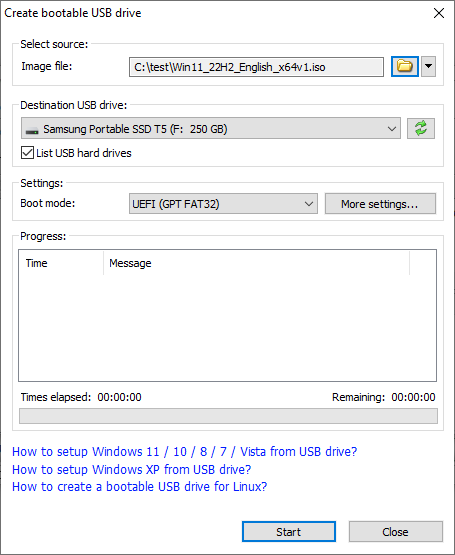
- PowerISO will alert you that all data on USB drive will be destroyed. Click "OK" to continue.
The program will start writing USB drive, and showing the progress information. You should get the message "Writing USB drive completed successfully." after the operation completes.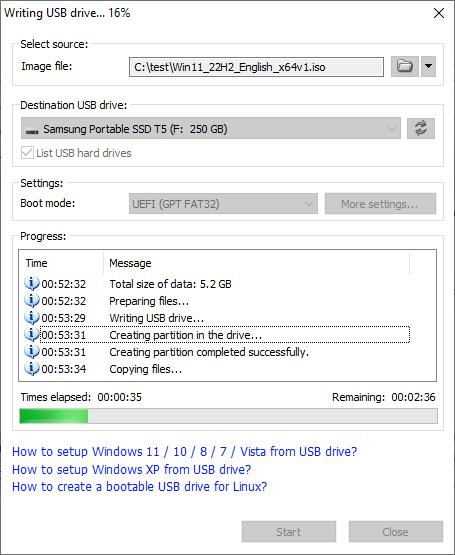
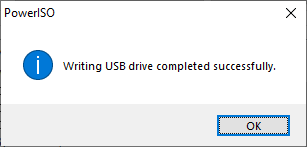
If no errors occurred in the above process, you should now be all set to setup Windows from USB drive!
Step 2: Configuring the BIOS
You should now reboot and go into the BIOS configuration to boot from USB. Instructions for doing so wildly from system to system, but generally entail the following:
- Reboot the system.
- While booting (before Windows starts loading), get into the BIOS configuration screen by hitting something like F1, F2, Delete or Escape. Hotkey instructions are generally provided on the screen.
- Go to the section that contains your boot devices.
- With your USB drive plugged in, the USB drive should be listed. If it isn’t, your system might not support booting from USB. Assuming that it is supported (as is the case with virtually all modern hardware), promote your USB drive to the primary boot device.
- Exit from the BIOS configuration, saving all changes.
Please notice that you can seriously screw up your system by providing incorrect BIOS settings!
Step 3: Booting and setup windows from USB drive
Assuming that you properly configured your BIOS and your USB drive supports booting, Windows setup should now load. Depending on the speed of your USB drive, this may take a while.
If it isn’t working, then double-check the following before making a scene:
- Is your BIOS properly configured for booting from the USB device? (Is the USB device listed and does it have top priority?)
- Have you correctly prepared the USB drive in step one? (Restart the procedure.)
- Does your USB drive properly support being booted from? (Try another one!)
Comments
Post a Comment